De wereld van de verschillende fascia.
Er wordt veel over fascia gesproken en er zijn diverse therapieën en massages die zich op een of andere manier specifiek met fascia bezighouden.
Omdat fascia bindweefsel is is het een structuur die uiteraard binnen de osteopathie een belangrijke plaats inneemt en er is een heel groot assortiment aan specifieke fascia technieken die in de osteopathie gebruikt worden.
Er zijn zelfs osteopaten die hier in het bijzonder op gespecialiseerd zijn.
Osteopathie houdt zich met vooral bezig met de mobiliteit van bindweefsel in de ruimste zin, dus alle anatomische en fysiologische verbanden zijn belangrijk hierin. Fascia zijn dus bindweefsel maar waar heb je het over als het over de verschillende fascia hebt.
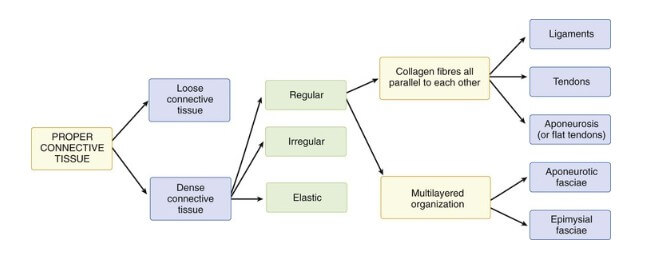
Carla Stecco functional atlas of the human fascial system
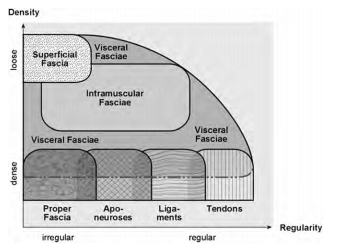
Uit: FASCIA SCIENCE AND CLINICAL APPLICATIONS: NOMENCLATURE REVIEW : Rober Schleip 2012
Volgens het “Fascia Congress Brussels 2012″ zijn de volgende definities neergelegd voor de verschillende fascia
Ik heb de originele Engelse tekst laten staan met daaronder de Nederlandse vertaling.
(I kept the original english text in the definitions)
Dense connective tissue
- Connective tissue containing closely packed, irregularly arranged (that is, aligned in many directions) collagen fibers.
- Bindweefsel dicht bijeengepakt , onregelmatig gerangschikt (in veel verschillende richtingen opgelijnd), collagene vezels
Non-dense (areolar) connective tissue
- Connective tissue containing sparse, irregularly arranged collagen fibers.
- Los(mazig) bindweefsel, bevat spaarzaam, onregelmatig aangelegd collageen weefsel.
Superficial fascia
- Enveloping layer directly beneath the skin containing dense and areolar connective tissue and fat.
- Oppervlakkige fascia, een omhullende bindweefsellaag direct onder de huid dat compact- en los bindweefsel en vet bevat
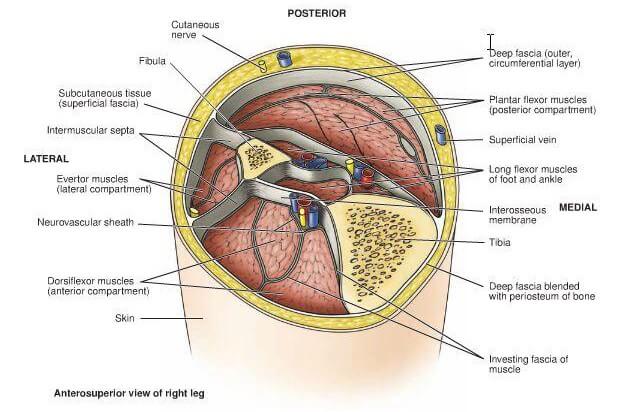
Overzicht van de verschillende fascia in het onderbeen
Deep fascia
- Continuous sheet of mostly dense, irregularly arranged connective tissue that limits the changes in shape of underlying tissues.Deep fasciae may be continuous with epimysium and intermuscular septa and may also contain layers of areolar connective tissue.
- Diepe fascia, een continue vlies van meestal compact onregelmatig gerangschikt bindweefsel die veranderingen in vorm van onderliggende weefsels aflijnen.
Intermuscular septa
- A thin layer of closely packed bundles of collagen fibers, possibly with several preferential directions predominating, arranged invarious layers. The septa separate different, usually antagonistic, muscle groups (for example, flexors and extensors), but may notlimit force transmission.
- Intermusculaire vliezen (aflijningen), een dunne laag van dicht bijeen gepakte bundels collageen weefsel, mogelijk in diverse voorkeurs richtingen (functioneel). Gerangschikt in diverse lagen. De septa (aflijningen), scheiden verschillende, meestal antagonistische spiergroepen (bijv fexoren,extensoren), maar limiteren nimmer kracht overdracht.
Interosseal membrane
- Two bones in a limb segment can be connected by a thin collagen membrane with a structure similar to the intermuscular septa.
- Membrana interossea, een dun collageen vlies tussen twee functioneel belendende botstukken, gelijkend op intermusculaire septa.
Periost
- Surrounding each bone and attached to it is a bi-layered collagen membrane similar in structure to the epimysium.
- Periost is het bot omringende vlies dat bilaminair is en vergelijkbaar met epimisium (buitenste vlies om een groep spierbundels).
Neurovascular tract
- The extramuscular collagen fiber reinforcement of blood and lymph vessels and nerves. This complex structure can be quite stiff.The diameter and, presumably, the stiffness of neurovascular tracts decrease along limbs from proximal to distal parts. Their stiffness isrelated to the angle or angles of the joints that they cross.
- Neurovasculaire tractus, extramusculair collageen versterkte weefsels die zenuwen bloed- en lymfe vaten (gezamenlijk !) omvatten.Het is een complexe structuur, vaak vrij stijf en verminderd in doorsnede van proximaal naar distaal. The stijfheid is gerelateerd aan hoek waaronder bijvoorbeeld gewrichten gekruist worden).
Epimysium
- A multi-layered, irregularly arranged collagen fiber sheet that envelopes muscles and that may contain layers of both dense andareolar connective tissue.
- Epimysium, een meerlagig, onregelmatig aangelegd collagen vlies dat spieren aflijnd (omvat), het bevat zowel dicht als los bindweefsel.
Intra- and extramuscular aponeurosis
- A multilayered structure with densely laid down bundles of collagen with major preferential directions.The epimysium also covers the aponeuroses, but is not attached to them.Muscle fibers are attached to intramuscular aponeuroses by their myotendinous junctions.
- Intra en extra musculaire aponeurosen, een meerlagige vliesstructuur met compact neergelegde collagene vezels met een duidelijke richtings voorkeur (functioneel) Het epimysium lijnt ook de aponeurosen af, maar is hier niet aan vastgehegt, De spierweefsels verlopen via musculotendinogene overgangen in de aponeurosen.
Perimysium
- A dense, multi-layered, irregularly arranged collagen fiber sheet that envelopes muscle fascicles. Adjacent fascicles share a wall ofthe tube (like the cells of a honeycomb).
- Perimysium, een dicht meerlagig gerangschikt collageen vlies. Dat de spierbundels omvat, aanliggende vliezen vormen samen een honingraatstructuur.
Endomysium
- Fine network of irregularly arranged collagen fibers that form a tube enveloping and connecting each muscle fiber.Adjacent muscle fibers share a wall of the tube (like the cells of a honeycomb).
- Een zeer fijn network van onregelmatig geranschikt collageenvlies dat een aflijning vormt rond iedere spiervezel, ook deze structuur vormt aansluitend een honingraatstructuur.
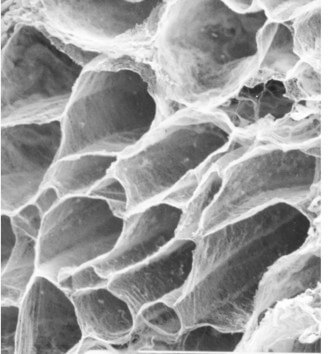
endomysium
In onderstaande bronnen is veel inhoudelijk te vinden over structuur en functie van de verschillende fascia
Jaap van der Wal The architecture of the connective tissue in the musculoskelletal system (fascia congres Brussel 2012)
Robert Schleip Tensional network of the human body
en What is ‘fascia’? A review of different nomenclatures
http://fasciaresearch.de/Schleip2012_FasciaNomenclatures.pdf
Carla Stecco functional atlas of the human fascial system
revisie:
Dit document werd 07-11-2016 aangepast met A review of different nomenclatures pdf

